Even though Fed Chair Jerome Powell remarked that it’s too soon to definitively conclude that rate hikes are finished, the financial markets have, in fact, decided they’re finished. As of December 4, 2023, interest-rate futures traders (the people who make a lot of money being right about where rates will go) expect the Fed to cut the federal funds rate, which currently falls between 5.25% and 5.50%, by 1.25%.
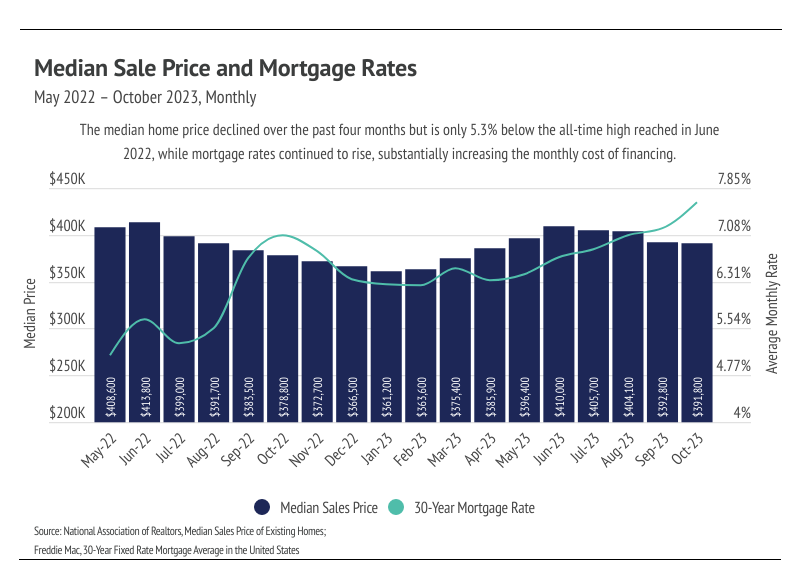
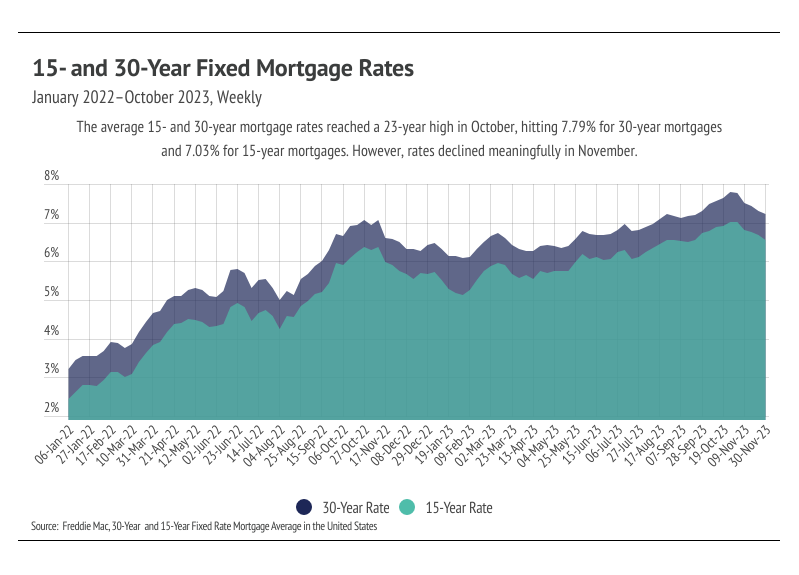
As a quick recap, the Fed dropped the fed funds rate effectively to 0% at the start of the pandemic and purchased mortgage-backed securities. The already historically low average 30-year mortgage rate then fell even further, reaching a record low of 2.65% in early 2021, which fueled the housing boom from June 2020 to June 2022. Inflation spiked in 2021, hitting levels not seen since the early 1980s and causing the Fed to begin rate hikes in March 2022, which trickled through markets quickly. From the beginning to the end of 2022, mortgage rates more than doubled, ending the white hot housing market and creating the slow-paced 2023 market. Mortgage rates continued to rise in 2023, hitting a 23-year high of 7.79% in October. Luckily, the average 30-year mortgage rate contracted in November 2023, falling to 7.22% by the end of the month.
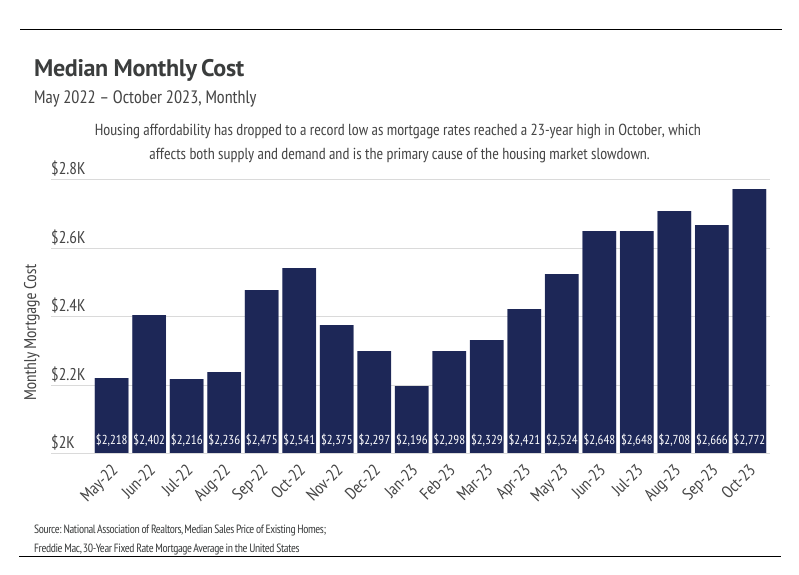
It’s hard to convey the full significance of higher mortgage rates on the housing market but, in short, they are the primary driver of the market slowdown. This is evidenced by the fact that the market began slowing down at almost the exact same time that the Fed began their rate hikes. In October 2023, a buyer’s monthly cost reached an all-time high when accounting for the cost of financing a mortgage. Redfin reported the highest rate of buyers backing out of home purchases on record, as home buyers experienced the sticker shock of the cost to finance the home. It should come as no surprise that sales continued to fall and will likely continue to decline through the winter months.
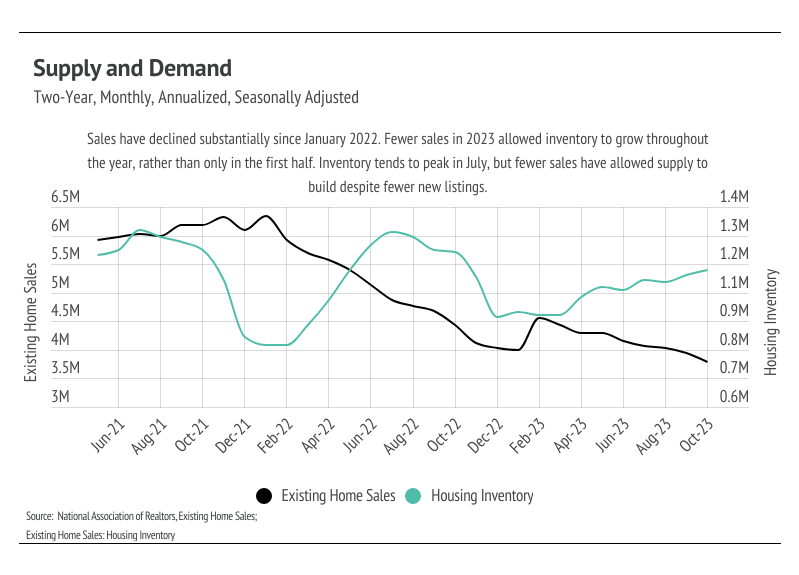
Now, back to our outlook for the year ahead. The falling sales in 2023 have allowed inventory to grow, which is much needed. Although inventory is still down 6% year over year, it has increased 20% in 2023 and will likely continue to increase through the rest of the year, which is far different from the typical seasonal trend of increasing in the first half of the year and declining in the second. In Q1 2024, we expect inventory to rise further, helping ease the low supply problem. Greater supply will be necessary because mortgage rates should decrease meaningfully with the anticipated rate cuts, driving up demand. A 1% decrease in interest rate equates to a 10% decrease in monthly financing costs. At this point, we expect a large number of would-be buyers to wait a little longer to gain more clarity around rate cuts in 2024 and hit the market in the spring and summer months.
Different regions and individual houses vary from the broad national trends, so we’ve included a Local Lowdown below to provide you with in-depth coverage for your area. In general, higher-priced regions (the West and Northeast) have been hit harder by mortgage rate hikes than less expensive markets (the South and Midwest) because of the absolute dollar cost of the rate hikes and limited ability to build new homes. The National Association of Realtors’ Chief Economist Lawrence Yun recently remarked that multiple offers are still occurring, especially on starter and mid-priced homes, even as price concessions are happening in the upper end of the market. As always, we will continue to monitor the housing and economic markets to best guide you in buying or selling your home.
Big Story Data
The Local Lowdown
-
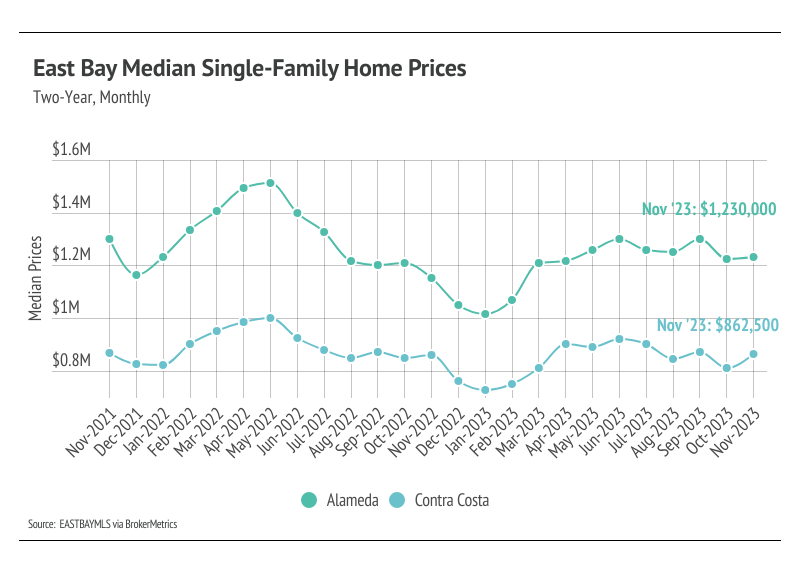
The median single-family home price rose in the East Bay in November, staying in line with the six-month horizontal price trend. We expect that trend to continue until interest rates drop and more sellers come to the market.
-
Active listings, sales, and new listings fell month over month for single-family homes and condos. Inventory will likely decline more for the next few months before rising in the spring.
-
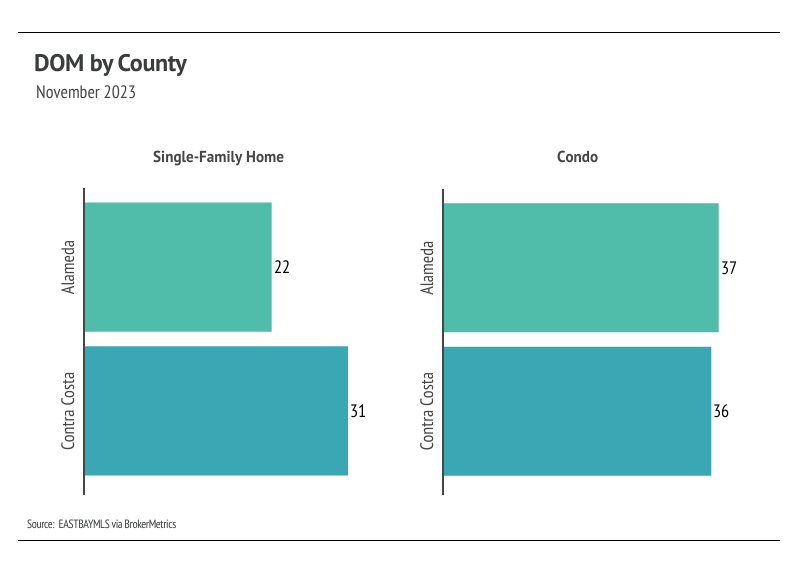
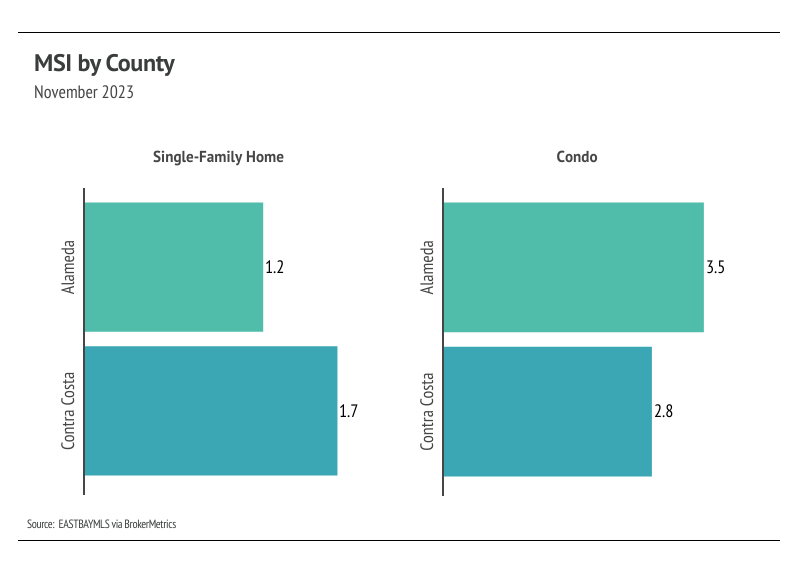
Months of Supply Inventory indicates the single-family home market still strongly favors sellers, but the condo market shifted more toward balance. It’s common for MSI to trend higher in the fall and winter, when fewer buyers are in the market and sales slow.
Note: You can find the charts/graphs for the Local Lowdown at the end of this section.
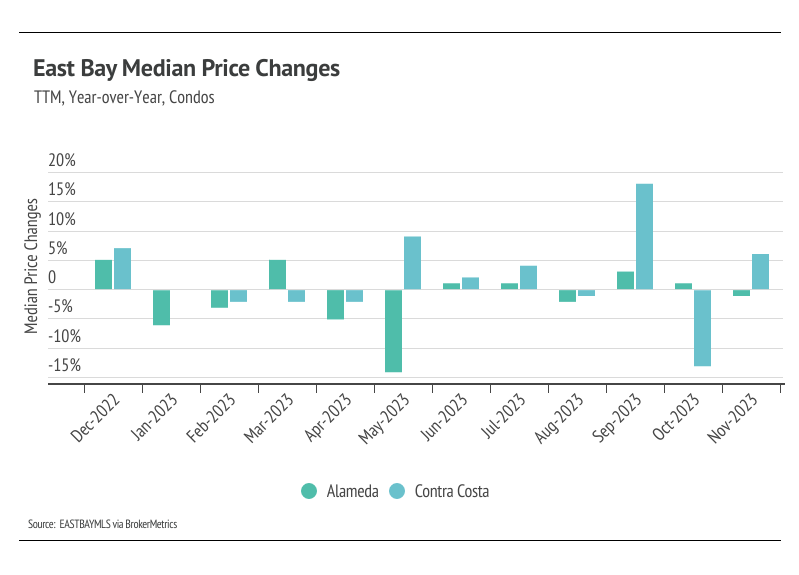
Prices increase across most of the East Bay in November
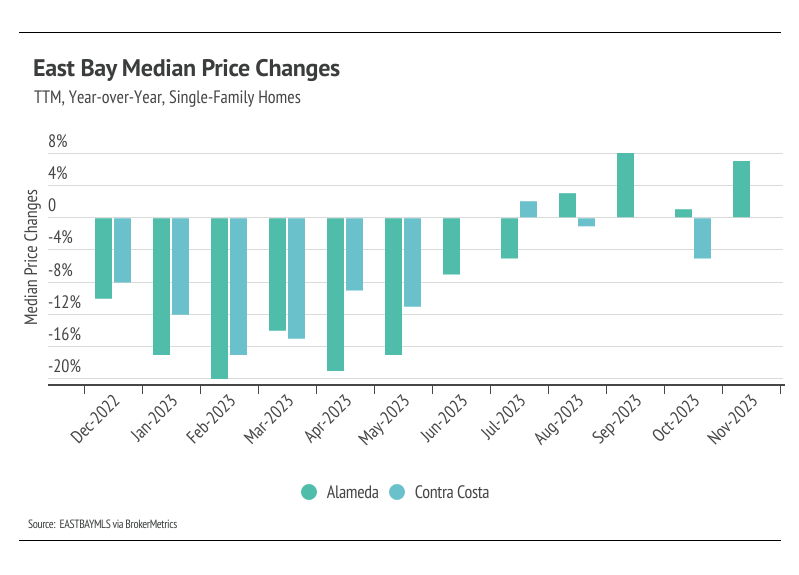
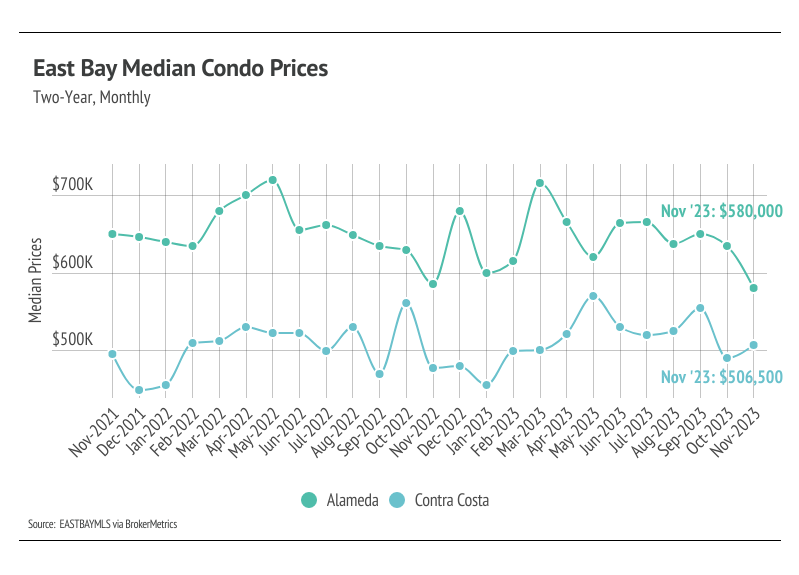
In the East Bay, home prices haven’t been largely affected by rising mortgage rates after the initial period of price correction from May 2022 to January 2023. Month over month, in November, the median single-family home price rose 0.4% in Alameda and 6.2% in Contra Costa. Condo prices were more mixed, with a 9.6% decline in Alameda and a 3.1% gain in Contra Costa.We expect prices to remain fairly stable in the winter months, but as interest rates decline and more sellers come to the market, prices will almost certainly rise in the first half of 2024. More homes must come to the market in the spring and summer to get anything close to a healthy market.
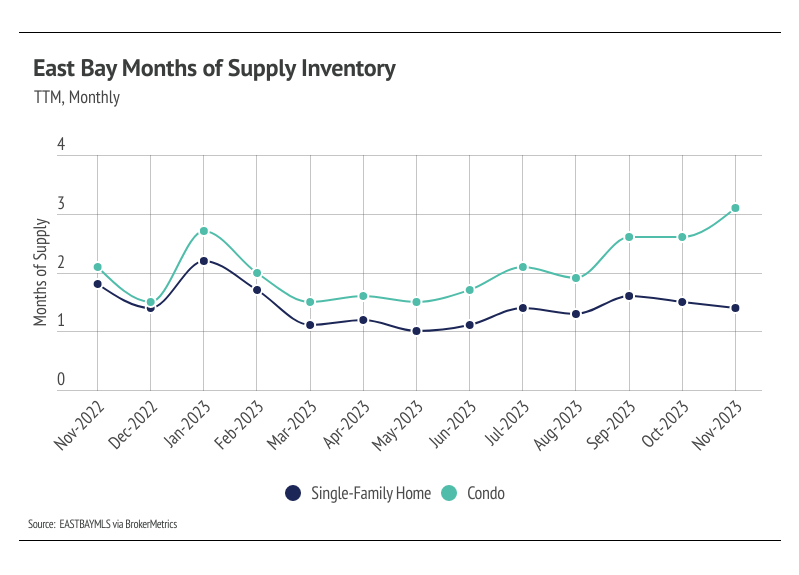
High mortgage rates soften both supply and demand, so ideally, as rates fall, far more sellers will come to the market. Rising demand can only do so much for the market if there isn’t supply to meet it. Unlike 2023, 2024 inventory has a much better chance of following more typical seasonal patterns.
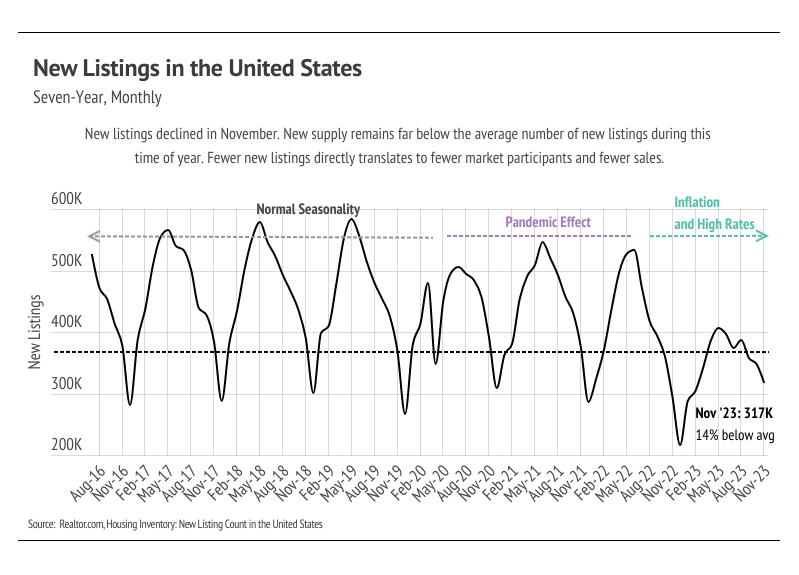
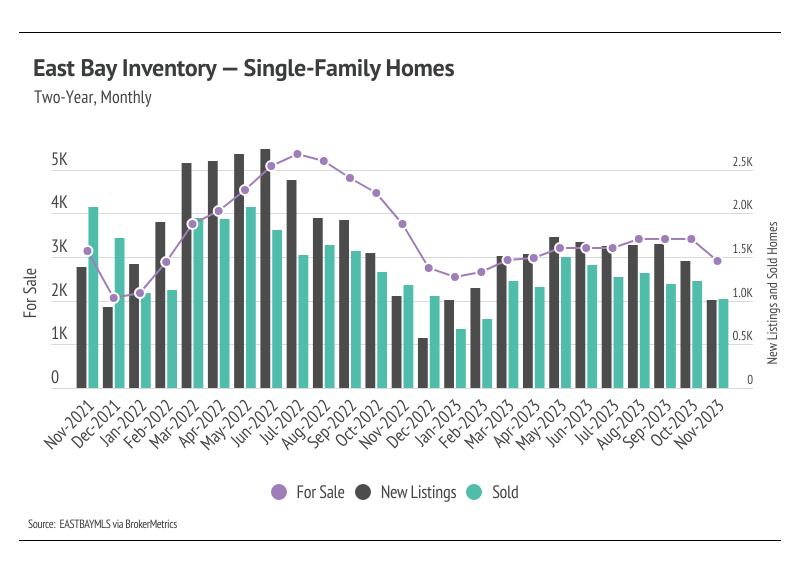
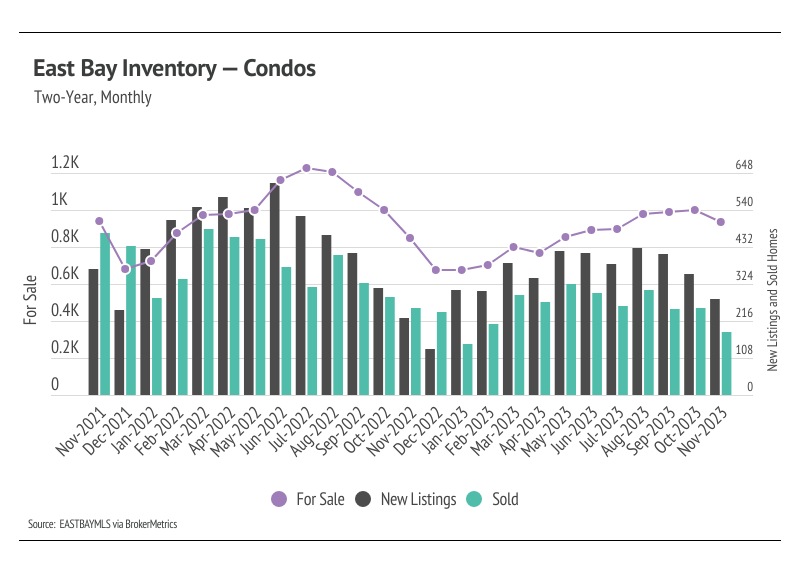
Inventory, sales, and new listings declined month over month
Single-family home and condo inventory barely increased at all this year, which is far from the seasonal norm. In 2023, inventory didn’t have anything resembling the typical sine wave, since far fewer sellers came to the market, especially in the first half of the year, and the low inventory and fewer new listings have slowed the market considerably. New listings have been exceptionally low, so the little inventory growth this year was driven by softening demand. Typically, inventory peaks in July or August and declines through December or January. However, this year, inventory peaked in October, further highlighting the atypical supply trend. In November, inventory, sales, and new listings dropped, which is normal this time of year. With the current low inventory levels, the number of new listings coming to market is a significant predictor of sales. Month over month, new listings fell 29% and sales declined 18%.
As demand slows, buyers are gaining slightly more negotiating power and paying less than asking price on average. The average seller received 95% of list in January, which grew to 105% by June. The average amount received by sellers slowly declined to 102% of list from June to November 2023. Inventory will almost certainly remain historically low for the next few months, and buyer competition will ramp up meaningfully in the spring, which will create price support.
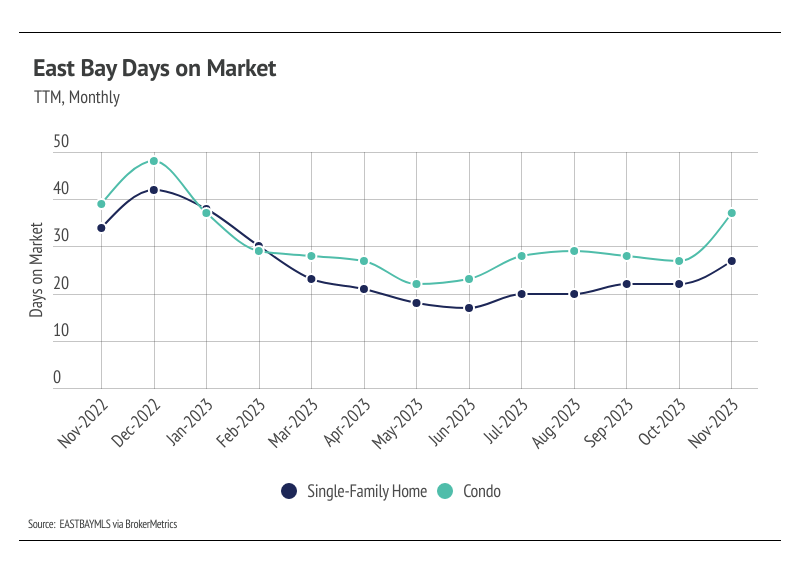
Months of Supply Inventory indicates the single-family home market still strongly favors sellers, while the condo market is more balanced
Months of Supply Inventory (MSI) quantifies the supply/demand relationship by measuring how many months it would take for all current homes listed on the market to sell at the current rate of sales. The long-term average MSI is around three months in California, which indicates a balanced market. An MSI lower than three indicates that there are more buyers than sellers on the market (meaning it’s a sellers’ market), while a higher MSI indicates there are more sellers than buyers (meaning it’s a buyers’ market). The East Bay market tends to favor sellers, which is reflected in its low MSI. Single-family homes continue to strongly favor sellers in the East Bay. However, condo MSI has increased significantly over the past three months, indicating the market has shifted from a sellers’ market into a more balanced market.