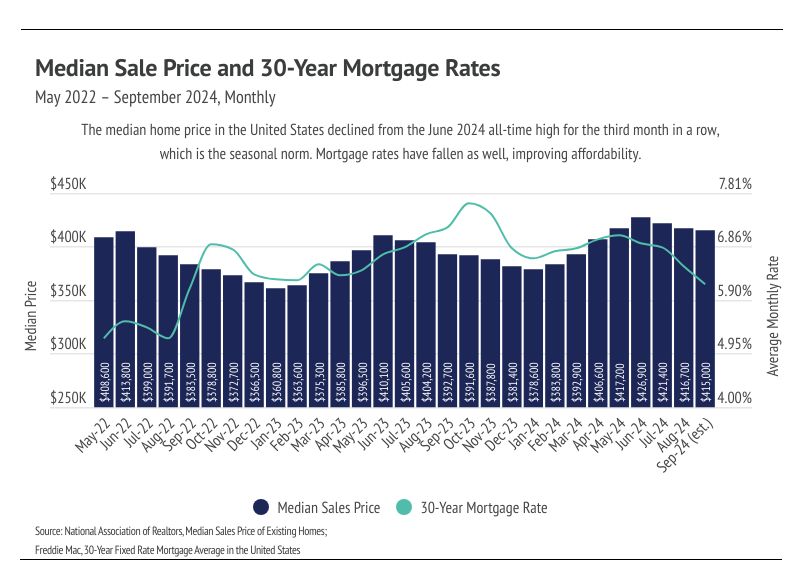
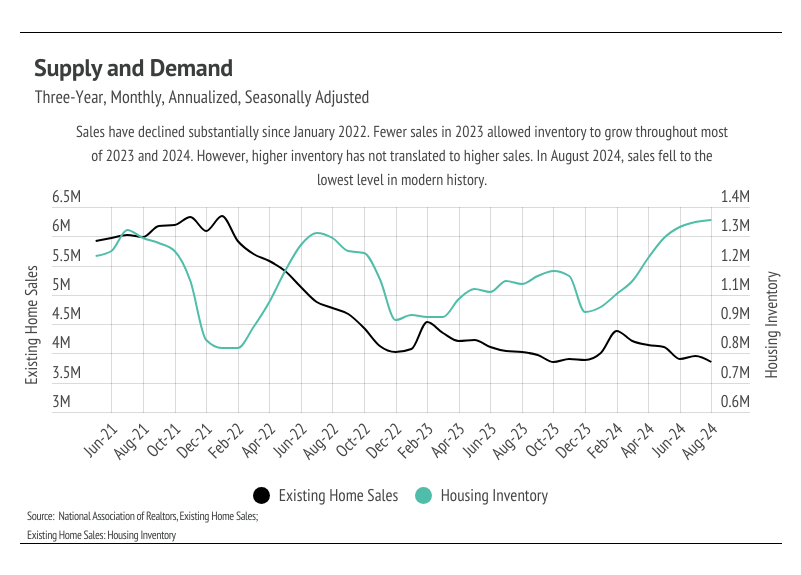
Enough data has been released to suggest that home prices peaked nationally in June 2024, and won’t peak again this year. Of course, there will be deviations in local markets, but the larger trend is clear: home prices are returning to a more normal growth and contraction cycle in which prices increase from January to June and contract from June to January. Sales have trended lower for nearly three years now, and that sales slowdown has allowed inventory to build to the highest level since 2020.
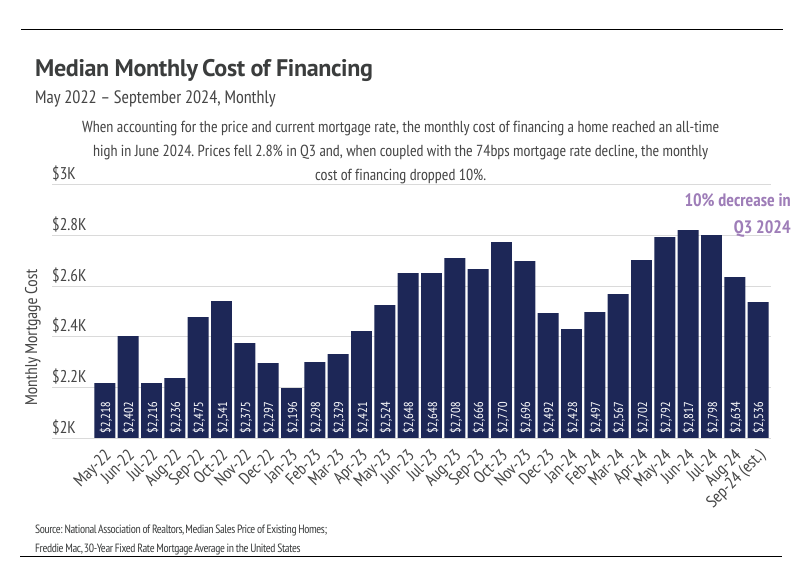
We were hopeful that sales would continue to increase this month due to the declining rates as it did last month, but sales fell to the lowest level in modern history. Even though the Fed lowered their benchmark rate by 0.50% at the September Fed meeting, mortgage rates weren’t largely affected, mainly because the rate cut was already priced into the current mortgage rates. In Q3 2024, the median price fell 2.8% and the mortgage rate declined by 74 bps, causing the payment on a monthly 30-year mortgage to drop 10%. Affordability is improving and the median home buyer saved $100,000 over the life of the loan, if they bought in September rather than June (a huge change in just three months!). Rate cuts and improved affordability are a promising sign as we look ahead to the spring market. We expect to enter 2025 with falling rates, high inventory, and seasonally lower home prices, which should create the perfect storm necessary for a hot spring market.
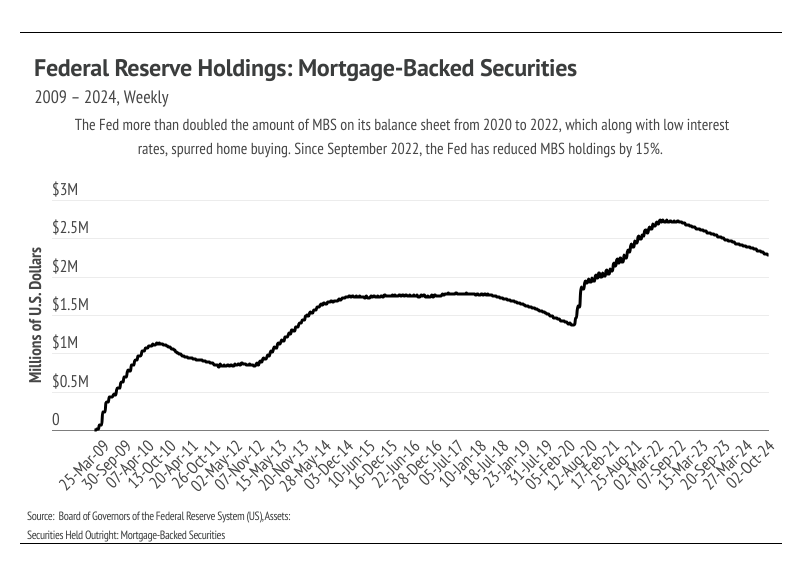
During the early pandemic, the Fed provided huge incentives to buy homes as part of its easy monetary policy by purchasing Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) and dropping interest rates. MBS play an integral role in home financing by allowing banks to bundle and sell mortgage loans, turning the bank into an intermediary between the financier and financial markets (investors). Banks get some fees, while investors (rather than the bank) get the interest and incur the risk from the bundle of mortgages. So, in many ways, the bank facilitates the loan but investors are the ones really lending the buyer the money. The Fed was a huge investor in 2020 and 2021, doubling its MBS holdings to $2.7 trillion by 2022. However, the Fed isn’t buying any more MBS and, in fact, has sold 15% ($4.16B) of its MBS holdings over the past two years. Even though rates are coming down, the MBS market has shifted to make loans less easy to originate, which has contributed to the market slowdown.
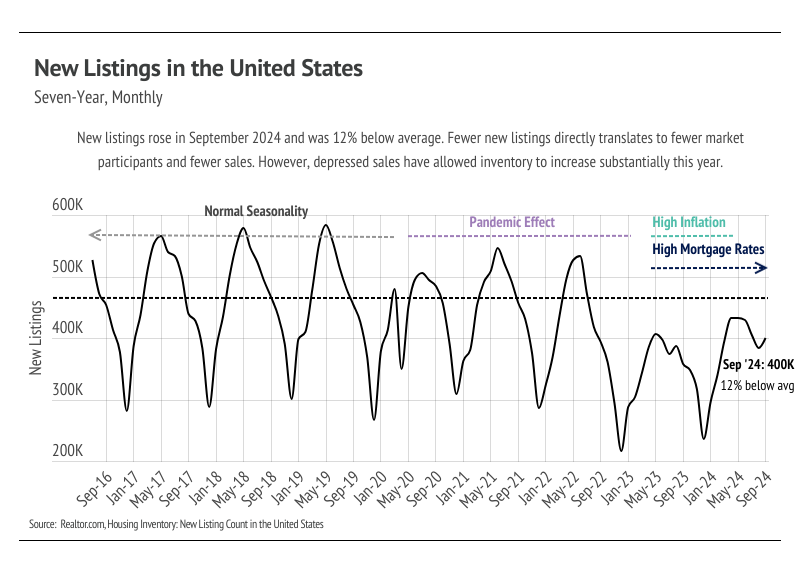
Last September, the average 30-year mortgage rate was 7.31%, meaning that a $500,000 loan would cost $3,431 per month. For reference, that same loan now costs $3,056 per month at 6.08%. Because the interest rate has such an outsized impact on the affordability of a home, fewer buyers entered the market, allowing inventory to build. Even though far fewer sales occurred over the past year, prices still rose, which they almost always do. This is actually a newer phenomenon, but one that isn’t going away. Since the mid-1990s, home prices began to move more like risk assets (stocks, bonds, commodities, etc.), which marked a huge change from the preceding 100 years. From 1890 to 1990, inflation-adjusted home prices rose only 12%, which is hard to imagine with the massive price growth, up 94% nationally, that we’ve seen over the past 10 years. All that to say, home prices over time really only move in one direction, which is up.
Different regions and individual houses vary from the broad national trends, so we’ve included a Local Lowdown below to provide you with in-depth coverage for your area. As always, we will continue to monitor the housing and economic markets to best guide you in buying or selling your home.
Big Story Data
The Local Lowdown
-
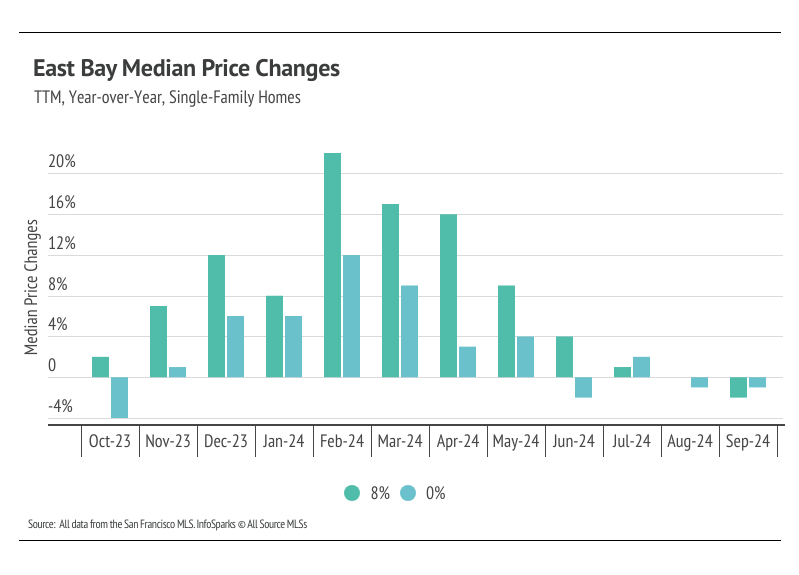
Median home prices are slightly below peak levels across the East Bay. We expected price contraction after peaking in the second quarter, which is the seasonal norm. Prices will likely decline for the rest of the year.
-
Total inventory rose 6.0% month over month, as new listings rose due to lower rates and more sellers coming back to the market. However, we expect inventory to decline and the overall market to slow in the fourth quarter.
-
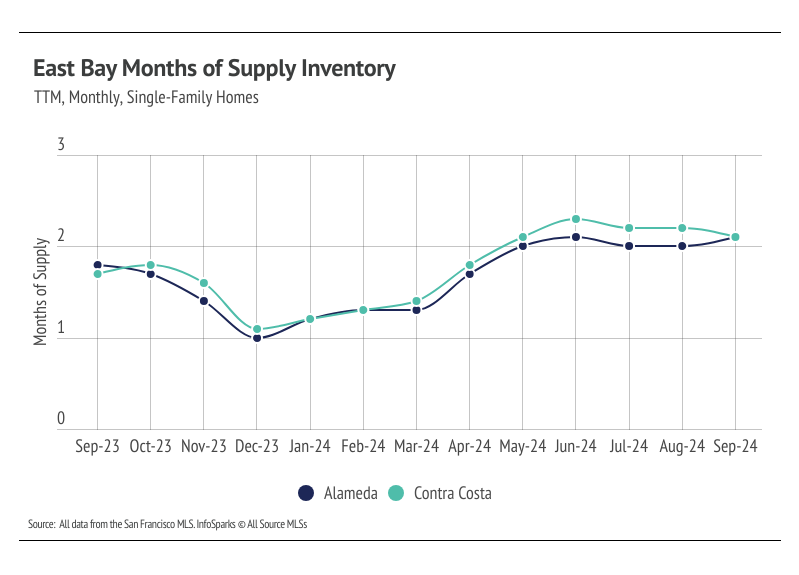
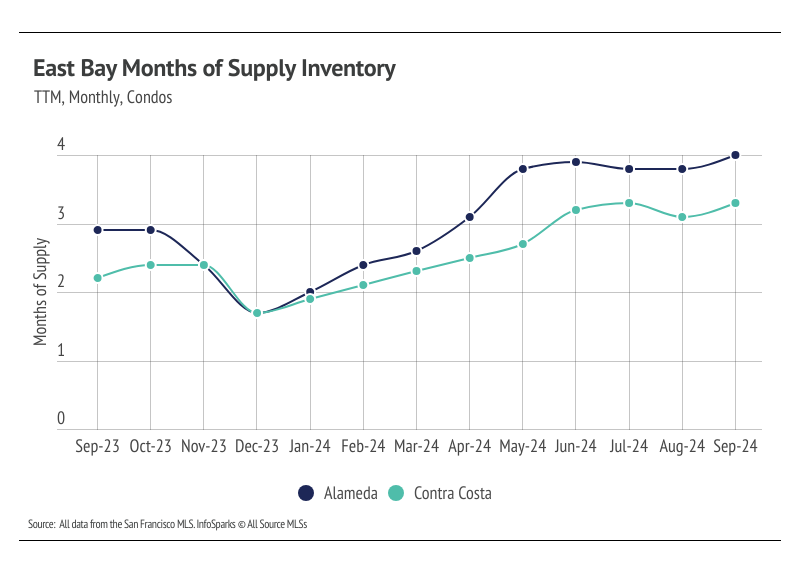
Months of Supply Inventory still indicates a sellers’ market in the East Bay for single-family homes, but for condos, MSI implies the market now favors buyers.
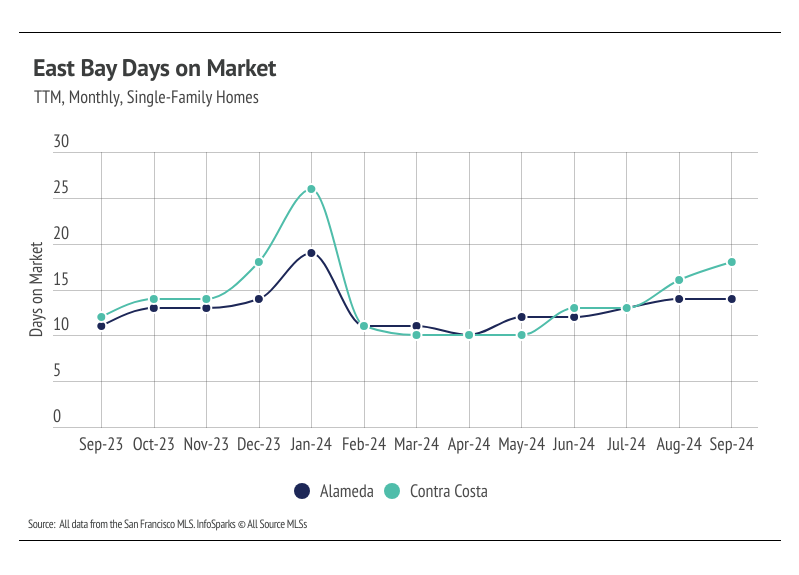
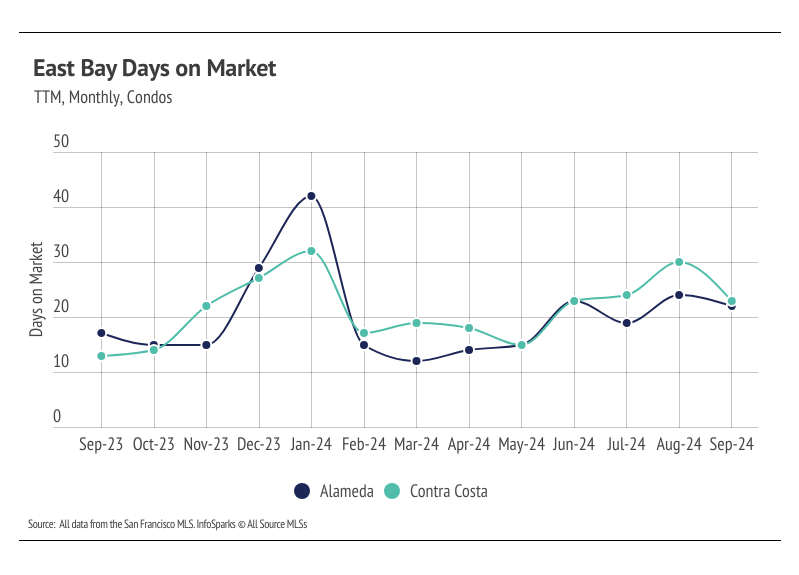
Note: You can find the charts/graphs for the Local Lowdown at the end of this section.
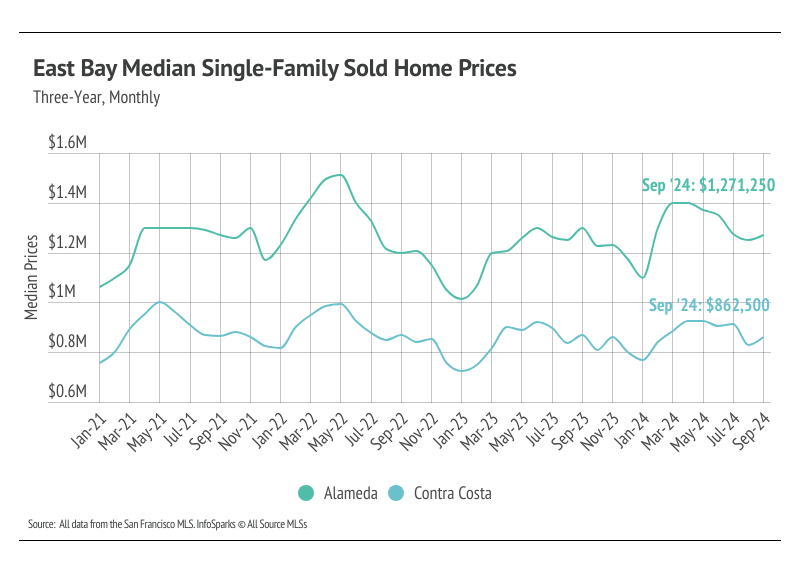
Median home prices rose month over month in the East Bay
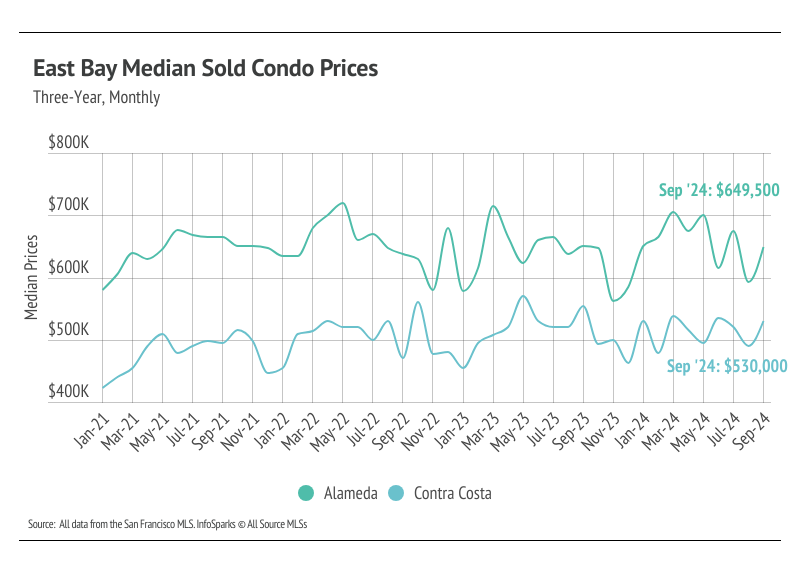
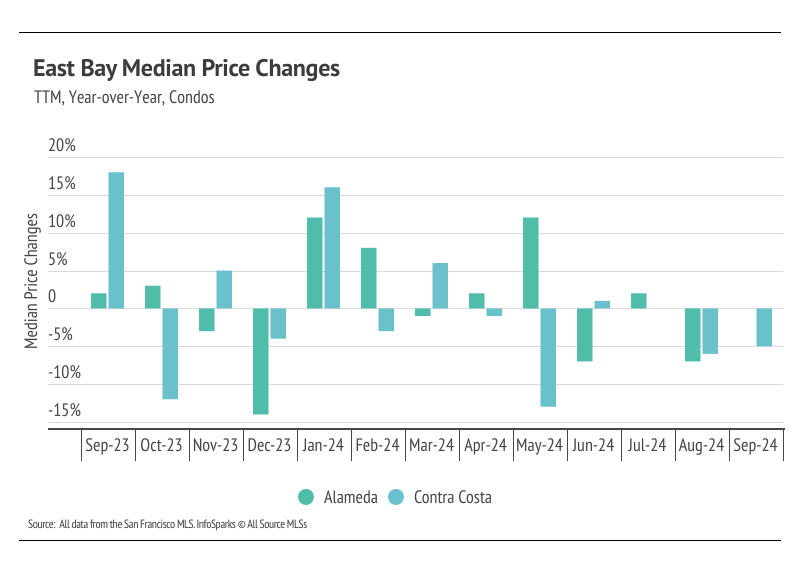
In the East Bay, home prices haven’t been largely affected by rising mortgage rates after the initial period of price correction from May 2022 to January 2023. Low, but growing, inventory and high demand have more than offset the downward price pressure from higher mortgage rates. Year to date, in September, the median single-family home and condo prices rose across the East Bay. For single-family homes, prices rose 8% in both Alameda and Contra Costa, and for condos, prices were up 11% in Alameda and 15% in Contra Costa. Year over year, however, prices are down slightly. Prices typically peak in the summer months, so we don’t expect new all-time highs for the rest of this year. However, we do expect some minor price contraction in the fourth quarter.
High mortgage rates soften both supply and demand, but home buyers and sellers seemed to tolerate rates near 6% much more than around 7%. Now that rates are declining, sales could get a little boost, but the housing market typically slows in the fourth quarter of any year.
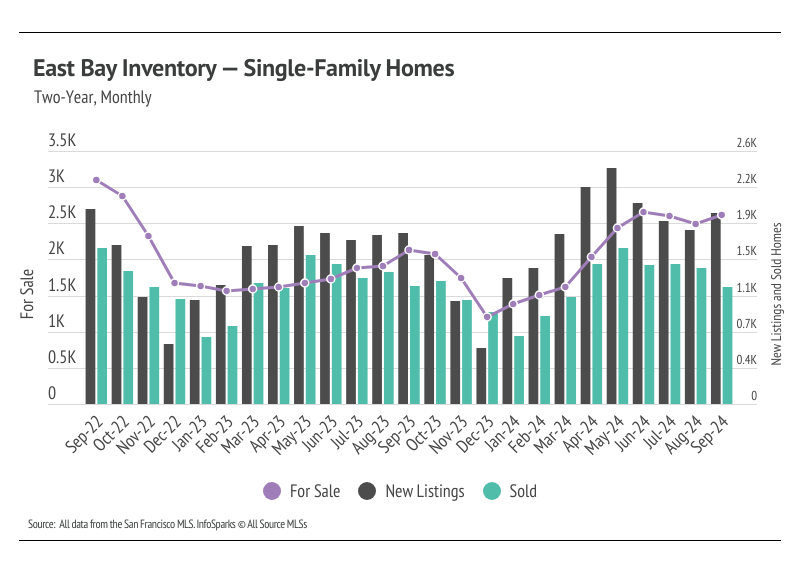
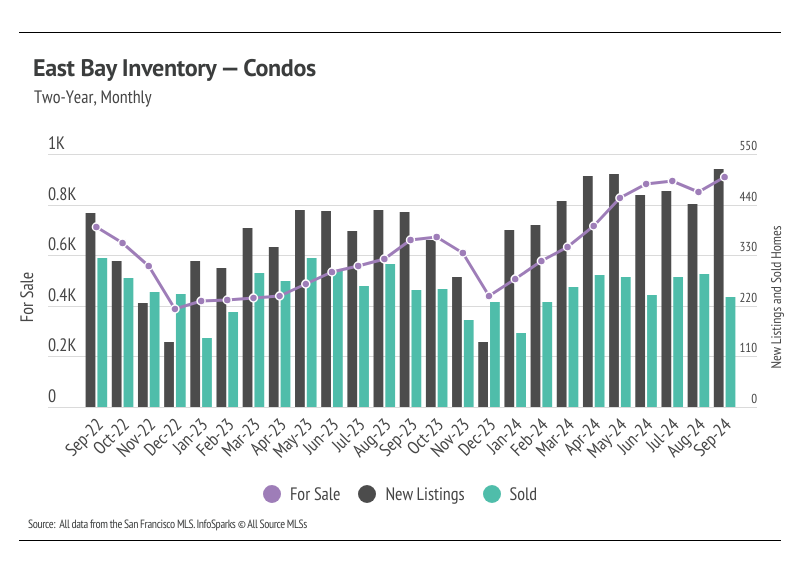
New listings rose in September, causing inventory to increase
The 2024 housing market has looked progressively healthier with each passing month. We’re far enough into the year to know that inventory levels are about as good as we could’ve hoped, although single-family home inventory is still lower than we would like. In 2023, single-family home and condo inventory followed fairly typical seasonal trends, but at significantly depressed levels. Low inventory and fewer new listings slowed the market considerably last year. Even though sales volume this year was similar to last, far more new listings have come to the market, which has allowed inventory to grow. Condo inventory even reached a four-year high in September. For single-family homes, inventory is up 24% year over year.
Typically, inventory begins to increase in January or February, peaking in July or August before declining once again from the summer months to the winter. It’s looking like 2024 inventory, sales, and new listings will resemble historically seasonal patterns, and at more normal levels than last year. However, inventory still increased in September, which is atypical. Falling mortgage rates have brought buyers and sellers back to the market during the time of year the market tends to slow significantly.
Months of Supply Inventory in September 2024 indicated a sellers’ market for single-family homes and a buyers’ market for condos
Months of Supply Inventory (MSI) quantifies the supply/demand relationship by measuring how many months it would take for all current homes listed on the market to sell at the current rate of sales. The long-term average MSI is around three months in California, which indicates a balanced market. An MSI lower than three indicates that there are more buyers than sellers on the market (meaning it’s a sellers’ market), while a higher MSI indicates there are more sellers than buyers (meaning it’s a buyers’ market). The East Bay market tends to favor sellers, especially for single-family homes, which is reflected in its low MSI. MSI has trended higher in 2024, causing condos to move from a sellers’ market to a buyers’ market. Although single-family home MSI has moved higher, it’s still low, indicating a sellers’ market.